- Where are U.S. drugs really made? A new Senate bill aims to find out (fiercepharma.com)
The vast majority of drugs that make it to American shelves are produced abroad, sometimes in countries that lawmakers worry don't have the nation's best interests at heart. But where are exactly are those drugs produced and how reliant is the U.S. on foreign imports? A new bipartisan Senate bill aims to find out.,,"The coronavirus pandemic has made it painfully clear that we must take decisive action to rebuild our nation's medical manufacturing sector," Rubio said. "This bipartisan bill would ensure policymakers have the necessary information to address our supply chain vulnerabilities, the consequences of foreign investment in U.S. pharmaceuticals, and reduce our over-reliance on China for pharmaceuticals."...The bill would require the FTC and Treasury to produce its report one year after it passes into law...READ MORE
- FDA will require 50% efficacy for COVID-19 vaccines. How high is that bar? (fiercepharma.com)Development and Licensure of Vaccines to Prevent COVID-19 Guidance for Industry (fda.gov)
Coronavirus vaccine developers now have some advice from the FDA: To win approval, any vaccine must be at least 50% effective in preventing the disease...FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn plans to roll out that guidance...It sets a bar about on par with a flu shot's performance in a good year—but it falls short of some expert recommendations for arresting the virus' spread...The agency also won’t approve a shot based on its ability to create antibodies in patients’ blood...Despite the urgency of this particular vaccine hunt, the FDA “will not reduce its standards or cut corners in its review to approve a vaccine,”...READ MORE
- Colorcon launches drug authentication platform (outsourcing-pharma.com)
The company’s SoteriaRx platform offers on-dose technology and detection services for authenticating a broad range of medications...(which)...protect patients from counterfeit products...on-dose authentication provides a powerful tool for tracking medicines from plant to patient and provides a level of supply chain authenticity and transparency not previously available. By incorporating microtags, the pill itself effectively becomes a barcode which can be digitally read and recorded, providing instant authentication...the incorporation of microtags essentially turns the pill itself into a barcode. This can be digitally read and recorded for authentication..READ MORE.
- High Prices Forcing Americans to Buy Prescription Drugs From Overseas (newsmax.com)Socioeconomic and Demographic Characteristics of US Adults Who Purchase Prescription Drugs From Other Countries (jamanetwork.com)
More than 2 million Americans buy prescription drugs from other countries as a way around rising prices in the United States, a new study finds...The analysis of nationwide survey data showed that 1.5% of adults got their prescription meds from outside the United States between 2015 and 2017...Immigrants and people who were older or who had inadequate health insurance coverage and tight budgets were more likely to do so. Those who use the internet for health care information were, as well, the findings showed...The number of Americans looking for cheaper prescription drugs is likely to rise due to the spike in unemployment stemming from the coronavirus pandemic and the loss of work-based health insurance...READ MORE
- FDA blasts California compounding pharmacy for facility ‘contaminated with filth’ (fiercepharma.com)
Auro Pharmacy has had a number of run-ins with FDA investigators...The FDA has had a long and troubled history with compounding pharmacies...sometimes those facilities bring it on themselves...Auro Pharmacies operated a veritable house of horrors at its...outsourcing facility, with ants in the sterile production areas and visibly dirty work surfaces, FDA investigators found during an August 2018 inspection...Those poor conditions could have produced supposedly sterile drugs that were "contaminated with filth,"...The FDA knocked Auro with a 10-observation Form 483 in August, 2018 that led to a voluntary recall of all the pharmacy's affected drugs and a stoppage to all sterile production...Even worse for Auro, the FDA followed up its August 2018 look-in with another round of inspections in September of last year that turned up most of the same sanitary issues, including "filth" on the end of hood-cleaning wands, and cracked and scratched production hoods...That inspection lead to a separate 11-observation Form 483 sent in October...READ MORE
- UCSF pays hackers $1.1M to regain access to medical school servers (fiercehealthcare.com)
Hackers extorted more than $1 million from the University of California, San Francisco after hitting its medical school servers with ransomware...On June 3, UCSF IT staff detected a security incident...Friday, the organization posted an update that it negotiated with the hackers to pay a portion of the ransom to regain access to the medical school servers..."The data that was encrypted is important to some of the academic work we pursue as a university serving the public good. We, therefore, made the difficult decision to pay some portion of the ransom, approximately $1.14 million, to the individuals behind the malware attack in exchange for a tool to unlock the encrypted data and the return of the data they obtained,"...READ MORE
- WHO lays out ambitious plan to deliver 2 billion coronavirus vaccine doses (biopharmadive.com)
The World Health Organization, together with partner organizations, aims to secure 2 billion doses of coronavirus vaccines by the end of 2021, unveiling...a creative plan to ensure high-risk groups around the world have access to any vaccine that's successfully developed... Through the WHO's plan, countries would be able to pool their resources to invest in the development a broad portfolio of experimental vaccines, obtaining in return a guaranteed share of the resulting supplies. The idea is to lessen the risk of betting on any one vaccine, while creating a mechanism by which doses are fairly allocated during the initial stages of a vaccine's availability...READ MORE
- FCC adds $198M for rural healthcare providers to boost telehealth services (fiercehealthcare.com)
The Federal Communications Commission is adding almost $200 million to a rural healthcare program to help providers buy telecommunications and broadband services...Rural healthcare providers have been hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic due to the loss in revenue from canceled or deferred elective procedures and the additional expense of personal protective equipment...At the same time, telehealth visits have surged as patients seek virtual care options during the pandemic. The Trump administration lowered regulatory barriers for rural areas. Physicians can care for patients at rural facilities across state lines and via telemedicine...And in many places—particularly rural areas that have the most to gain from telemedicine and connectivity—broadband remains too expensive, unreliable or simply not available at the speeds required to enable innovations in care...READ MORE
- From Parkinson’s to peanut allergy, pandemic puts brakes on new drugs (reuters.com)
Treatments for peanut allergy and Parkinson’s disease are among U.S. drug launches that have been postponed by the COVID-19 pandemic as drugmakers struggle with disruptions to business...The Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 30 new medicines since January, but at least five drugmakers...have changed their launch plans...Launching drugs is an expensive and complicated process that includes sales representatives talking to doctors, coordinating supplies and treatment with pharmacies and clinics, and advertising campaigns - many of which have become harder during lockdowns or other restrictions to tackle the pandemic...That’s bad news for patients and drugmakers...Delays altogether could cost companies over a quarter of the originally estimated more than $1 billion in 2020 sales for the products approved by the FDA since January...READ MORE
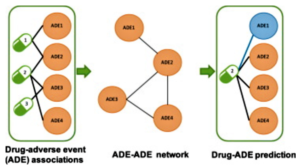
- New Machine Learning Tool Can Predict Adverse Drug Effects (drugtopics.com)Development of an adverse drug event network to predict drug toxicity (sciencedirect.com)
A new computer algorithm might be the next step toward accurate prediction of adverse drug reactions..Researchers from Harvard Medical School and the Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research announced the creation of an open-source machine learning tool capable of predicting drug adverse effects (Aes)...The study, published in The Lancet journal EBioMedicine, examined 2 databases: 1 that reported adverse drug reactions and another with 184 proteins that specific drugs are known to interact with. Investigators constructed a computer algorithm to develop associations between the drug reactions and the 184 individual proteins...The algorithm discovered 221 associations, some known and some new. These associations indicated which proteins contribute to certain AEs and which may not...The new algorithm could help predict these AEs before the drug goes to human clinical trials, as well as before and after it enters the market...READ MORE