- IBM pitched its Watson supercomputer as a revolution in cancer care. It’s nowhere close (statnews.com)
It was an audacious undertaking, even for one of the most storied American companies: With a single machine, IBM would tackle humanity’s most vexing diseases and revolutionize medicine...promoting its signature brand — Watson — IBM sought to capture the world’s imagination, and it quickly zeroed in on a high-profile target: cancer...But three years after IBM began selling Watson to recommend the best cancer treatments to doctors around the world, a STAT investigation has found that the supercomputer isn’t living up to the lofty expectations IBM created for it. It is still struggling with the basic step of learning about different forms of cancer. Only a few dozen hospitals have adopted the system, which is a long way from IBM’s goal of establishing dominance in a multibillion-dollar market...While it has emphatically marketed Watson for cancer care, IBM hasn’t published any scientific papers demonstrating how the technology affects physicians and patients. As a result, its flaws are getting exposed on the front lines of care by doctors and researchers who say that the system, while promising in some respects, remains undeveloped...
- University Collaborating With Israeli Cancer Research Company (ktvn.com)
The University of Nevada, Reno, is collaborating with an international company who is in the business of cancer treatment. They will be investing millions of dollars in better equipment at the College of Science (Nevada Terawatt Facility in Stead)...a...new venture with Israeli company HIL Applied Medical who is pouring millions of dollars into bringing UNR's "cheetah laser" to its full potential. They hope to find new ways to deliver proton therapy for cancer patients that is smaller, more effective and less expensive...This might scale into small and medium size hospitals like the ones we have in our local community here...Less than 5 percent of patients around the world have access to proton-therapy cancer treatment because equipment can cost upwards of $100 million. With this collaboration, they think they could get costs down to $1 million so it's a feasible option for more hospitals...Researchers from HIL Applied Medical will visit Reno often to conduct tests alongside Terawatt Facility technicians. As they move forward, the company anticipates creating more jobs in Reno...
- Computer-Simulated Tests Eyed at FDA to Cut Drug Approval Costs (bloomberg.com)
Computer simulations may get a role alongside human testing as part of an effort to bring new medications and medical devices to market more quickly and cheaply...The...Food and Drug Administration outlined a proposal...to help integrate computer modeling and virtual testing as part of the regulatory approval process for manufacturers -- a step the agency said could save money while helping find cures for puzzling conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease...The average cost of developing a new medication is about $2.56 billion...and much of that goes to fulfilling the FDA’s rigorous demands for proving safety and effectiveness...The price of new technology affects the ability of people to access these new treatments...We therefore need to be mindful of the costs of our regulatory processes, to the degree that these costs also affect the availability of new innovations, and the way that they are ultimately priced…The idea of computer simulated experiments, sometimes called in silico trials, has been around for years but the FDA hasn’t provided guidance to allow the drug industry to use it in testing...The FDA has begun using computer modeling to build databases to help researchers predict how new treatments...will perform. And the agency is developing a family of "virtual patients" for testing new devices…
- New Pain Drug Likely To Face Price Challenges From Payers (forbes.com)
Centrexion Therapeutics announcing six-month data with its drug, CNTX-4975, for the treatment of moderate to severe knee osteoarthritis pain. The results are from a Phase 2b trial...and Centrexion is pretty excited by what has been seen so far:..The new data show large and statistically significant pain relief...a single 1 mg injection...resulted in large levels of pain reduction compared to baseline and statistical separation from placebo...These data represent the largest reductions seen in knee osteoarthritis reported for any drug treatment, marketed or in development…the active component is capsaicin...CNTX-4975 is "based on Centrexion’s proprietary STRATI technology (Synthetic TRans cApsaicin ultra-pure Injection), a highly potent, ultrapure, synthetic form of trans-capsaicin."...In certain ways, CNTX-4975 is reminiscent of the EpiPen. The active component of the latter is epinephrine, which, like capsaicin, is a drug that’s been known for decades. It’s the injector device, however, and not the drug, that drives Mylan’s proprietary position–and price–for the EpiPen. Similarly, the STRATI technology is what protects CNTX-4975 competitively, as anyone can easily access trans-capsaicin. In addition, epinephrine and trans-capsaicin are cheap drugs. These aren’t complex biologic molecules...The major cost will be for the STRATI technology...it is possible that Centrexion and its investors are going to demand premium pricing for the unprecedented pain relief...How will payers react?
- First Gene-Transfer Therapy Approved for U.S. Market (ashp.org)Pioneering cancer drug, just approved, to cost $475,000 — and analysts say it’s a bargain (statnews.com)
FDA...announced the approval of tisagenlecleucel, a first-in-class chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy consisting of genetically modified autologous T cells, for the treatment of B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children and young adults...After modification in the laboratory and infusion back into the patient, the CAR T cells target and eliminate both normal and malignant CD19-expressing B cells. The genetic modification enhances the initiation of T-cell activation and the persistence of the transformed T cells...Novartis will market tisagenlecleucel as Kymriah. Labeling for the product states that it is indicated in patients up to age 25 years with ALL that is refractory or in second or later relapse...Tisagenlecleucel has an FDA-required risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program that includes elements to assure safe use. The labeling states that the immunotherapy is available "only through a restricted program."...
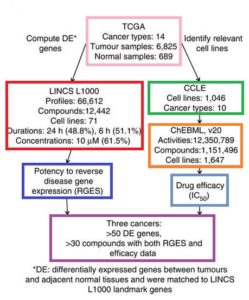
- Big-Data Analysis Points Toward New Drug Discovery Method (technologynetworks.com)Reversal of cancer gene expression correlates with drug efficacy and reveals therapeutic targets (nature.com)
A research team led by scientists at UC San Francisco has developed a computational method to systematically probe massive amounts of open-access data to discover new ways to use drugs, including some that have already been approved for other uses...The method enables scientists to bypass the usual experiments in biological specimens and to instead do computational analyses, using open-access data to match FDA-approved drugs and other existing compounds to the molecular fingerprints of diseases like cancer. The specificity of the links between these drugs and the diseases they are predicted to be able to treat holds the potential to target drugs in ways that minimize side effects, overcome resistance and reveal more clearly how both the drugs and the diseases are working...Our hope is that ultimately our computational approach can be broadly applied, not only to cancer, but also to other diseases where molecular data exist, and that it will speed up drug discovery in diseases with high unmet needs...I’m (Bin Chen, PhD) most excited about the possibilities for applying this approach to individual patients to prescribe the best drug for each...
- How AI Is Transforming Drug Creation (wsj.com)
Pharmaceutical companies hope computers can help them find new medications that are faster, cheaper—and more likely to be effective...The idea is that machines, which are adept at pattern recognition, can sift through vast amounts of new and existing genetic, metabolic and clinical information to unravel the complex biological networks that underpin diseases. That, in turn, can help identify medications likely to work in specific patient populations, while simultaneously steering companies away from drugs that are likely to fail...In the past, drug companies have used artificial intelligence to examine chemistry—whether a drug might bind to a particular protein, for instance. But now the trend is to use AI to probe biological systems to get clues about how a drug might affect a patient’s cells or tissues...Biological insights driven by machine learning also could help pharmaceutical companies better identify and recruit patients for clinical trials of therapies most likely to work for them, perhaps boosting the chances of those medications’ getting approved by regulatory agencies...The big difference between AI-driven drug trials and traditional ones...is "we’re not making any hypotheses up front. We’re not allowing [human] hypotheses to generate data. We’re using the patient-derived data to generate hypotheses."
- UNLV School of Medicine invests $600,000 in virtual anatomy (businesspress.vegas)
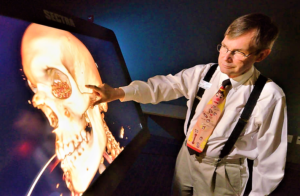
The UNLV School of Medicine is breaking with traditional teaching methods when the school’s 60 medical students start their anatomy class in November...Instead of using cadavers for dissections of the human body, the school invested $600,000 in the use of virtual technology. Students will learn anatomy by using virtual anatomy tables with large, interactive touch screens that are large, super high-resolution computer screens. They cost $100,000 each...The school describes them as body images in a wide variety of perspectives. They are primed with a library of images, such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans and pathology slides...Students will be able dissect, rotate, slice, and reassemble organs and other anatomic structures as needed. They will download case studies of real patients and examine them. They also can explore the histology and histopathology of the organ systems studied… UNLV will be the first allopathic medical school to use virtual 3-D anatomy...This is a very innovative way of doing this...No one else in the country has attempted to do what we’re doing. We’re cutting-edge at this point...
- Study Indicates 75% of Human Genome is Non-functional (technologynetworks.com)
An evolutionary biologist at the University of Houston has published new calculations that indicate no more than 25 percent of the human genome is functional. That is in stark contrast to suggestions by scientists with the ENCODE project that as much as 80 percent of the genome is functional...In work published online in Genome Biology and Evolution, Dan Graur reports the functional portion of the human genome probably falls between 10 percent and 15 percent, with an upper limit of 25 percent. The rest is so-called junk DNA, or useless but harmless DNA…this new study...will help to refocus the science of human genomics...“We need to know the functional fraction of the human genome in order to focus biomedical research on the parts that can be used to prevent and cure disease,” he said. “There is no need to sequence everything under the sun. We need only to sequence the sections we know are functional.”
- Value-Based Care Increasing the Popularity of mHealth (ajpb.com)
Mobile health has become increasingly popular as the healthcare world moves towards value and away from volume, according to a new study by GBI Research. mHealth can connect patients with numerous healthcare services, while also collecting valuable data...This approach has already had an impact on the healthcare industry and numerous organizations are making investments in the technology. mHealth can also be used to encourage patients to adhere to their treatments, providing physicians with an additional way to communicate beneficial behaviors to their patients... advances in mobile technology, the expansion of communication, and the reduction in the cost of wireless technology...have huge potential to bridge the gap within existing healthcare systems, offering an alternative form of healthcare communication and treatment at a distance...The most important driver behind mHealth is the growing need for cost-effective ways to provide healthcare...Another important driver is the shift towards value-based care and reimbursement...healthcare providers are interested in helping patients achieve optimal outcomes rather than being incentivized to order more tests or perform more services.