- IBM receives patent that could accelerate discovery of more effective and safer drugs (drugstorenews.com)
IBM...announced its scientists have been granted a patent ("Method and system for exploring the associations between drug side-effects and therapeutic indications") on machine learning models to predict therapeutic indications and side effects from various drug information sources, which could accelerate discovery of more effective and safer drugs...IBM Research has implemented a cognitive association engine to identify significant linkages between predicted therapeutic indications and side effects, and a visual analytics system to support the interactive exploration of these associations...this approach could help researchers in pharmaceutical companies to generate hypotheses for drug discovery...strongly correlated disease-side-effect pairs identified by the patented invention could be beneficial for drug discovery in many ways. One could use the side-effect information to repurpose existing treatments (e.g. drugs causing postural hypotension could be potential candidates for treating hypertension). If a new drug is being designed for a disease that is strongly correlated with severe side effects, then special attention could be paid to controlling the formulation and dosing of the drug in the clinical trials to prevent serious safety issues...Lack of efficacy and adverse side effects are two of the primary reasons a drug fails clinical trials, each accounting for around 30% of failures...Computational models and machine learning methods that can derive useful insights from large amounts of data on drugs and diseases from various sources hold great promise for...improving the drug discovery process.
- How a Major Drugmaker Plans to Cure Disease… Without Drugs (fool.com)
Hacking into the body's nervous system may allow GlaxoSmithKline to commercialize an entirely new field of medicine...GlaxoSmithKline plc has the resources to pursue long-term bets in medicine that could eventually change the course of disease treatment and yield large payoffs...to literally eavesdrop on the body's electrical system and enter into the body's own internal conversations in order to heal disease...every organ has a nerve connection that regulates its function. Organs are controlled by patterns of electrical impulses transmitted through nerve fibers, but when organs dysfunction in chronic disease, the electrical patterns are different. That fact opens up the possibility that inserting patterns in nerves to certain organs can correct conditions that lead to disease...scientists are just beginning to realize the possibilities of using nerve signals to restore organs to normal function and actually treat disease...Bioelectronic medicines have the potential of doing to the pharmaceutical industry what biopharmaceuticals did to small molecules back in the 1980s…
- DNA computer brings ‘intelligent drugs’ a step closer (worldpharmanews.com)
Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology present a new method that should enable controlled drug delivery into the bloodstream using DNA computers. In the journal Nature Communications the team...describes how it has developed the first DNA computer capable of detecting several antibodies in the blood and performing subsequent calculations based on this input. This is an important step towards the development of smart, 'intelligent' drugs that may allow better control of the medication for rheumatism and Crohn's disease, for example, with fewer side-effects and at lower cost...An analogy for the method presented…is a security system that opens the door depending on the person standing in front of it. If the camera recognizes the person, the door unlocks, but if the person is unknown, the door remains locked. "Research into diagnostic tests tends to focus on the 'recognition', but what is special about this system is that it can think and that it can be connected to actuation such as drug delivery...
- Life-extending capacity of new cancer drugs varies widely (reuters.com)
Drugs recently approved around the world to fight cancer increased patients' overall survival, but benefits vary depending on the drug, a new study shows...Researchers looked at the 62 cancer drugs approved in the U.S. and Europe between 2003 and 2013 and found they extended survival by an average of about 3.5 months...a third of the drugs lacked evidence to suggest they increased survival when compared to alternative treatments...results point to the notion that new cancer treatments may not always provide patients with greater clinical benefits, or lower risks, over existing treatments...The risk-benefit ratio of new drugs is especially important if people are concerned, for example, about whether the cost of a drug would make it difficult for a person to complete the treatment regimen...
- The First CAR-T Drugs Have Left the Gate (fool.com)
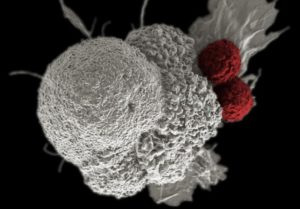
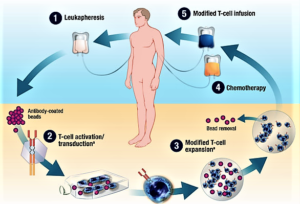
Investors should keep an eye on this promising way to treat cancer...For all the talk about biotechs being nimble, it's a big pharma that looks like it'll be the first company to launch a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) product...Novartis announced last week that the Food and Drug Administration accepted its application to market tisagenlecleucel-T...in patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are relapsed and refractory to other therapies...A few days later, Kite Pharma completed its application for axicabtagene ciloleucel...Kite's application could be accepted early, putting it less than two months behind Novartis…Since CAR-T therapies are personalized treatments that have to be made individually for each patient, they're likely to be expensive to produce and therefore require a premium price. The first company to get a CAR-T therapy approved will set the price, which later companies may have to match unless they can justify a higher price with higher efficacy...With prices that will probably exceed those of current cancer treatments, investors should expect some pushback from insurers. One way Novarits and Kite can get around the cost issue is by offering money-back guarantees...Kite's and Novartis' CAR-T therapies are just the tip of the iceberg for this new way to treat cancer...
- Tech-focused Takeda pilots Apple Watch trial to collect depression data (fiercepharma.com)
Wearable tech is increasingly making its way into pharma, and Takeda is welcoming the trend with open arms. Most recently, the Japanese drugmaker partnered with digital health tools venture Cognition Kit to collect active and passive patient data for a deep dive on depression...Each person in the just-launched pilot study will wear an Apple Watch that will passively collect physical activity data all day, while three separate prompts throughout the day will remind the patients to complete cognitive and mood assessments...Results from the study, which are expected in the first half of the year, will look at the wearable mood and cognition measurements, along with compliance, and compare the findings to more traditional examinations and patient-reported assessments... This collaboration is part of our strategy to embrace new technology to better understand the patient experience and assist healthcare professionals in creating improved patient care pathways...
- Broad Institute notches win in CRISPR patent battle (biopharmadive.com)
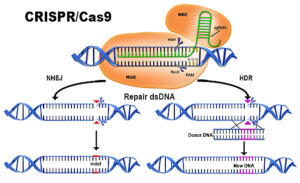
In a hotly anticipated judgment, the U.S. patent office...ruled that key patents held by the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard on the gene-editing technology CRISPR-Cas9 do not overlap with competing claims from the University of California...UC may now receive a patent covering broader claims on the revolutionary tech...the Patent Trial and Appeal Board ruled the claims of UC and the Broad to be patentably distinct subject matter, leading the three judges to declare a judgment of non-interference...Put into layman's terms, the claims of the UC and the Broad are distinct enough so as to be separately patentable and therefore don't overlap with each other. This effectively supports the Broad's existing patents, while sending the UC's pending patent application back to the initial patent examiner...UC with a patent on use of CRISPR in all cells and the Broad with a patent for use of CRISPR specifically in eukaryotic cells...If that were to happen, biotechs operating in the space could end up having to license the tech from both UC and the Broad.
- 20,000 leagues for biotech to explore (biopharmadive.com)
The sea covers around 70% of the earth, and contains around 97% of the world's water. It's also home to almost 240,000 species...as a resource, it is still untapped...Bioprospecting is the discovery and development of new products based on resources from the natural world...We are not marine organisms, so until about 1970, no one even thought of the ocean. It was left as a deep secret. It seemed ridiculous to me that the ocean — with such a vast habitat — had escaped anyone's notice. But there are good reasons. People fear the ocean; it has been considered a very hostile, inhospitable place...the history of drugs from the sea isn't particularly long. Red algae have traditionally been used to make a treatment for colds, sore throats, chest infections including tuberculosis, kidney trouble, burns, cancer and indigestion...There are plenty of high-profile drugs that have gotten their origins from the sea…There are more than 25 marine-derived molecules in clinical trials, with over a thousand in pre-clinical development...There are still many societal challenges that the marine environment could help us to meet, such as antibiotic resistance...It is a source of chemical diversity, with novel targets and novel modes of action...
A snapshot of late stage development:
- PharmaMar...Plitidepsin and lurbinectedin, both derived from sea squirts... T-cell lymphoma...
- BeyondSpring...linabulin...is based on a marine fungus…non-small cell lung cancer...
- Ohr Pharmaceutical...Squalamine...found in dogfish shark tissues...a wide variety of indications…antimicrobial against bacteria, fungi, protozoa and viruses, as well as in cancer, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and fibrodysplasia ossificans progressive...
- Wex Pharmaceuticals...puffer fish...neurotoxin tetrodotoxin...a non-addictive and rapid-acting pain killer without opioid-like side effects....
- Trump Care Will Create A New Wave Of Digital Healthcare Opportunities (forbes.com)
The next few years are likely to see a major attempt to use market mechanisms to reduce the cost of U. S. healthcare. Healthcare costs are rising again, and Republican campaign promises will put huge pressure on the federal budget. Republicans prefer market based solutions to problems, and they harshly criticize the parts of Obamacare that expand health insurance participation by means of entitlements and sanctions...they feature a shift from defined benefit federal health programs like Medicare and Medicaid, which entitle individuals to the care they need mostly at government expense, to defined payment programs that give individuals a fixed payment based on their life status and leave them responsible for buying the care they need…Since the beginning of the digital health era, entrepreneurs have been interested in creating businesses that enable healthcare consumerism...Healthcare consumerism is very hard to pull off. Price data is still hard to access, understand, and compare...I suggest these guiding principles for entrepreneurs seeking to ride the new wave of healthcare consumerism:
- Choose a sector with favorable characteristics: one in which consumers can judge the value of one offering relative to another and, given choices with different prices, they can choose better value without great risk or inconvenience.
- Consider business models that give healthcare consumers the benefit of professional buyers acting on their behalf.
- ...bear in mind that there are many opportunities in digital healthcare beyond business models that enable healthcare consumerism...businesses focused on making healthcare more efficient by other means, or solving long-standing problems of patient outcomes, comfort, safety, and convenience stand to do well...
- IBM Watson and FDA to develop secure ‘blockchain’ patient data sharing (pharmaphorum.com)
IBM Watson is to work with the FDA to investigate the use of blockchain technology, seen as one of the most secure ways of sharing patient data...(it) allows each separate patient data source to be a ‘block’ part of a complete, unalterable patient data profile which can then be shared securely with healthcare providers or research organisations...Initially focused on oncology-related data, the collaboration will look at how best to exchange data gathered from multiple owner mediated data sources such as Electronic Medical Records, clinical trials, genomic data, mobile devices, wearables, and Internet of Things technologies...The deal aims to overcome the limitations of large scale sharing of health data seen in the past, namely data security and patient privacy concerns during the data exchange process.