- Allscripts subsidiary 2bPrecise looks to inject genomics into EHR workflow for precision medicine (healthcareitnews.com)
...2bPrecise (subsidiary of Allscripts) is conducting an early adopter program at the National Institutes of Health...The goal is to take clinical and genomic information and make it actionable, structured, machine-readable and machine-learning for physicians. And then take those results and inject the relevant information back into workflows...We focus on the last mile of genomics and cross-collating clinical info with genomics and bring it to the point-of-care...With NIH, we’re putting this to the test and demonstrating the value of genomics in clinical and research activity…People are recognizing genomics is needed, powerful and useful...What’s missing are regulations and reimbursement around this type of data. As healthcare continues to move into this space, I think we’ll see another spike in interest, with a huge level of interest and motivation to try to use genomics more…
- This is how 3-D bioprinting companies are transforming drug development (medcitynews.com)
... cells generally like having company, forming communities with other cell types to make complete tissues. However, quite often, researchers isolate cells from their 3-D environments, creating 2-D models that don’t always replicate complex biology...But now, an entire industry is emerging to recapitulate various tissues more realistically. 3-D bioprinting has the capacity to layer different cell types, creating more biologically accurate liver, kidney, skin and even tumor tissues. The hope is that more lifelike tissues will produce better scientific results...Organovo is the leader in 3-D bioprinting...The...company has been selling 3-D liver tissue to pharma companies for about 18 months and is about to expand into kidney tissue. The goal is to support drug development by using these 3-D models to gauge toxicity...Kidney and liver toxicology studies are required for every product before it goes into humans....The high costs of clinical trials could eventually make this a go-to technology for pharma and biotech, providing better data to spot toxicity early and avoid costly mistakes…
- Putting the cost of medicines in context (catalyst.phrma.org)
Discussions about costs are important. No patient should have to worry about whether they can afford the care they need. At the same time, it is important to look at costs across the health care system and not just the share going toward life changing medicines...new therapies are transforming care for patients fighting debilitating diseases like cancer, hepatitis C, high cholesterol and more. In the midst of all this progress, the share of spending on retail medicines remains the same as it was 50 years ago. In fact, government actuaries project the share of health care spending attributable to medicines will continue to grow in line with overall health care cost growth for at least the next decade...Our updated Prescription Medicines: Costs in Context explains how competition among brand-name medicines, high generic utilization rates and aggressive tactics by insurers and pharmacy benefit managers to negotiate lower prices all help to keep costs under control...
- Precision medicine market to skyrocket past $87 billion (healthcareitnews.com)
Cancer treatments, drug discovery, genome sequencing...are all driving big spending for personalized and precision medicine...Driven by demand for personalized medicine in cancer treatments and advancements in new healthcare technologies, the precision medicine market is expected to reach $87.79 billion by 2023, according to a report by Global Market Insights...Revenue growth will be sustained by favorable government regulations and standards...The trend toward an individualized diagnosis approach is growing thanks to large-scale biologic database development, efficient methods for patient characterization, and computational tools to analyze large data sets...Recent research advances have helped expand benefits to various aspects of healthcare by enabling better understanding of disease mechanisms, assessment of disease risks and prediction of optimal therapy...A large number of investments in diagnostic research will further accelerate the shift from treatment to preventive medicine in healthcare...
- New Big Data Approach Predicts Drug Toxicity in Humans (weill.cornell.edu)
Researchers can now predict the odds of experimental drugs succeeding in clinical trials, thanks to a new data-driven approach developed by Weill Cornell Medicine scientists. The method detects toxic side effects that may disqualify drugs from human use, giving drug developers an early warning before initiating clinical trials, according to a new study...The approach upends conventional wisdom about the criteria on which to evaluate new drugs for their safety. Rather than exclusively examining molecular structure to determine viability, this new computational method combines a host of structural features and features related to how the drug binds to molecules in the body...We looked more broadly at drug molecule features that drug developers thought were unimportant in predicting drug safety in the past. Then we let the data speak for itself…The method, known as PrOCTOR, was inspired by an approach that baseball statisticians adopted to better predict which players would be successful offensively...a strategy known as "Moneyball."...Similarly, researchers developed a computational method that analyzes data from 48 different features of a drug — from molecular weight to details about its target — to determine whether it would be safe for clinical use...this approach could improve the drug discovery pipeline, save money and save lives — but only if more data on toxicity results become available. After all, only 50 percent of clinical trial results are fully reported...if we don't have data, we can't build these models...
- Exploiting body’s fat absorption pathways may improve drug efficacy (upi.com)Glyceride-Mimetic Prodrugs Incorporating Self-Immolative Spacers Promote Lymphatic Transport, Avoid First-Pass Metabolism, and Enhance Oral Bioavailability (abstract) (onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
Many medications are broken down before making it to the bloodstream, preventing their arrival at the site of infection, but researchers think they've found a way to improve drug delivery by bypassing certain bodily processes...Researchers...have created a method of delivering drugs using the lymphatic system in order to bypass the liver and create a route directly to the bloodstream, increasing the amount of a substance making it to target areas...The advantage of our system is that drugs are shielded from degradation in the liver but are ultimately released when they reach their site of action, ensuring that the drug given to the patient goes where it is supposed to...researchers created a technology to modify drugs so they mimic dietary lipids, which are absorbed into the lymph system -- unlike other nutrients...No matter how good the drug is, it needs to be absorbed [into the bloodstream] and to avoid this first pass metabolism in order to get to the general circulation where it acts...
- The FDA just greenlit releasing mutant Zika-killing mosquitoes in Florida (fusion.net)Spraying Begins in Miami to Combat the Zika Virus (nytimes.com)Zika in the United States, explained in 9 maps (vox.com)
...the Food and Drug Administration gave the okay to a field trial that would release genetically modified Zika-killing mosquitoes in the Florida Keys...the FDA released a final environmental assessment of the trial, finding that it “will not have significant impacts on the environment.” The project, led by Oxitec, a biotech company that focuses on insect control, calls for the release of thousands of genetically engineered male Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. The lab insects are bred so that over time they could kill off much of the local mosquito population by passing on a gene fatal to any offspring they have with wild females...The FDA’s okay is a major step forward toward a U.S. implementation of the technology at a time of much concern over the spread of Zika in the U.S. after cases in Florida...
- Google, Sanofi launch joint diabetes venture (healthcareitnews.com)
The partners will develop a comprehensive diabetes platform and combine software, devices, medicine and professional care to improve diabetes management for patients...Verily Life Sciences, a subsidiary of Google’s parent company, Alphabet and Sanofi, a French multinational pharmaceutical company launched Onduo - a joint venture to improve diabetes care...The collaboration will leverage Verily’s miniaturized electronics, analytics and consumer software with Sanofi’s clinical expertise to create innovative treatments for diabetes patients…Onduo is designed to...help people with diabetes live full, healthy lives by developing comprehensive solutions that combine devices, software, medicine and professional care to enable simple and intelligent disease management...
- A Health-Monitoring Sticker Powered by Your Cell Phone (technologyreview.com)Battery-free, stretchable optoelectronic systems for wireless optical characterization of the skin (advances.sciencemag.org)
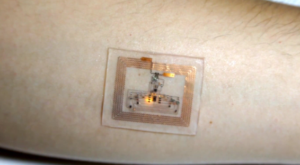
A wearable sensor measures blood oxygen using flashing LEDs. It's powered by radio waves from a nearby phone or tablet.
Stretchy electronics offer wearable health gadgets without batteries...Picture a health-monitoring patch you wear like a tattoo and that doesn’t need a battery...That’s the idea behind a demonstration by John Rogers, a stretchable electronics pioneer at the University of Illinois...whose lab created a stretchy skin patch that uses light pulses to monitor heart rate or sun exposure...it’s powered by a cell phone...with a near-field communications chip, the kind that’s used in apps like Apple Pay or for sharing photos between phones. That is, radio signals from a phone actually power the device and let it transmit information...Rogers says it means health-monitoring gadgets could be cheaper, smaller, and more lightweight than ever before...new device also measures heart rate and blood oxygenation using four LEDs to shine different colors of light into the skin. Changes to the color of the reflected light is picked up by photodetectors. A person’s heart rate is displayed as a flashing light.
- GSK and Google launch bioelectronics venture (pmlive.com)Q&A: Glaxo exec says bioelectronics is ‘not science fiction’ (statnews.com)
GlaxoSmithKline has joined forces with Google's Verily Life Sciences to establish a new company dedicated to the development of bioelectronic medicines...Galvani Bioelectronics - named for the 18th century Italian bioelectricity pioneer - will combine GSK's drug discovery and development expertise in disease biology with Verily's expertise in highly miniaturised technologies, including data analytics and software development for clinical application...Together, we can rapidly accelerate the pace of progress in this exciting field, to develop medicines that truly speak the electrical language of the body...Bioelectronic medicine is concerned with the electrical signals firing between the body's nervous system and organs, working to regulate the faulty nerve impulses that occur in many illnesses.








