- The Startup Tracking ‘Valuable’ Doctors for Big Pharma (bloomberg.com)
Physicians are worth billions of dollars to drugmakers, who see the prescription pad as a path to profits. But it’s growing harder for Big Pharma to get doctors’ appointments. Since 2010, Obamacare has slowly curbed the mass travel junkets and fancy meals that drug companies once used to sway the doctors most valuable to their efforts to sell products...Pharmaceutical companies are now searching for ways to refine their marketing efforts, to target the doctors most compatible with the medications they’re pitching. "You’re desperate for data to make those key decisions,"..."But while there’s lots of data out there, it’s really challenging to bring it together."...Zephyr Health...promising to help drugmakers identify key medical personnel and find ways to approach them…Zephyr builds digital dossiers on individual doctors. It starts with basic information on prescription patterns from data clearinghouses...Then its software...scours the Web for more details...Zephyr generates profiles that score each doctor’s influence and ability to drive sales on a scale of 1 to 10. The software’s slick, mobile-friendly interface lets a drug company search in broad or specialized disciplines and ranks each person’s influence in the chosen field. It also specifies whether a doctor appears to influence colleagues or simply writes a lot of scripts..."There’s nothing private anymore,"...While doctors may not be exactly psyched about Zephyr tracking their every move...even they should appreciate the company’s ability to narrow marketing campaigns. For a physician, "working with Pharma is akin to getting pecked to death by a flock of ducks," he says. "Do you want nine salespeople queued up to call on you?"
- New CRISPR/Cas9 delivery method could offer a clinical pathway (fiercedrugdelivery.com)Therapeutic genome editing by combined viral and non-viral delivery of CRISPR system components in vivo (Abstract, sub req) (nature.com)
CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing is a rapidly developing technique that is thought to provide revolutionary new ways to manipulate genes for the treatment of a number of diseases. Delivering the CRISPR therapeutic in an efficient, safe and predictable way, though, has been difficult--to this end, researchers at UMass have created a means of administering the gene editor that could help send it to clinical trials...CRISPR/Cas9 is a natural immune system in bacteria used to protect them from foreign genetic material, and scientists have used its components to cut and repair DNA sequences to replace faulty, disease-causing portions with corrected versions...The difficulty comes about in getting the separate components to the genetic material in a target cell. Previous attempts at delivering the system through disruptive, high-powered injection has caused damage to the liver...The new delivery method involves a two-part process. The researchers loaded both the CRISPR guide RNA and the DNA template into a viral vector...A week after the first injection, the scientists deliver the Cas9 messenger RNA wrapped in lipid nanoparticles...Until now it's not been possible to deliver CRISPR/Cas9 in a way that was suitable for clinical trials. By using an RNA guide and DNA repair template delivered via viral vector followed by a Cas9 in a lipid nanoparticle, we've take a huge step forward to overcoming this hurdle.
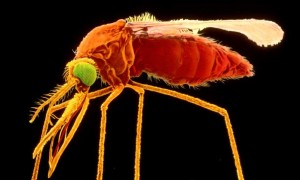
- We Can Beat Zika And Malaria–If The FDA Allows (forbes.com)The Emerging Zika PandemicEnhancing Preparedness (jama.jamanetwork.com)
Zika virus infection, the scary new disease for which there is no vaccine or treatment, is “spreading explosively” from Africa and Southeast Asia...The United States and 20 other countries...have reported cases of the virus since Brazil reported the first cases of local transmission last May. Delivered by varieties of mosquitoes...it has boosted interest in mosquito-borne diseases...What’s needed is...modern genetic engineering techniques to more effectively prevent mosquitoes from delivering the viruses and parasites that cause disease….The FDA has long delayed the approval of a November 2011 application for a field trial to test a new biological control agent for the mosquito species Aedes aegypti. Although that field trial is concerned specifically with dengue fever, A. aegypti...also transmits Zika...Oxitec has created a new way to control Aedes aegypti. Male mosquitoes are bred in the laboratory with a specific genetic mutation that, in the absence of a certain chemical, causes their offspring to die before reaching maturity...This safe and effective control technique has been approved in Brazil and open field trials of these mosquitoes have been conducted in Brazil, the Cayman Islands, Panama and Malaysia...Eight months have passed since FDA promised last May to publish for public comment a routine environmental assessment of the Oxitec field trial in Florida. Only after FDA reviews the comments will FDA consider whether to grant approval. This delay is unnecessary and unconscionable.
- Big Pharma’s bet on Big Data creates opportunities and risks (reuters.com)
Novartis wants every puff of its emphysema drug Onbrez to go into the cloud...The Swiss drugmaker has teamed up with U.S. technology firm Qualcomm to develop an internet-connected inhaler that can send information about how often it is used to remote computer servers known as the cloud...This kind of new medical technology is designed to allow patients to keep track of their drug usage on their smartphones or tablets and for their doctors to instantly access the data over the web to monitor their condition...It also creates a host of "Big Data" opportunities for the companies involved - with huge amounts of information about a medical condition and the efficacy of a drug or device being wirelessly transmitted to a database from potentially thousands, even millions, of patients...Wireless interfaces are a great benefit to certain patient groups...But...connectivity also means vulnerability...
- Mercy Health saves $42 million by tying list of approved medications to EHR (healthcareitnews.com)
...Mercy Health has saved more than $42 million on drugs since 2010 by building a formulary within its electronic health record platform...The move...makes it easier for the system’s network of providers to order medications that are on its list and compliant with Mercy’s pharmaceutical contracts...It took Mercy Health’s pharmacy and therapeutics committee three years to create the formulary -- a comprehensive list of medicines that Mercy Health would prescribe...Mercy places drugs in one of four categories:
- on the formulary and available from order sets;
- on the formulary but not available from order sets;
- restricted to a specific disease state or provider type;
- neither on the formulary nor in order sets.
These categories correspond to Mercy’s “bullseye” -- a visual representation of each medication class that committee members use to review their decisions...We generate reports on non-formulary drugs -- how many times they were ordered, and what the cost savings would be if we were to use a formulary drug instead...Mercy Health now has an average formulary compliance of more than 98 percent...The formulary management is most effective with a single EHR across the health system because it enables the health system to make modifications as their contracts change and to monitor compliance...
- Aprecia completes $35M financing to support launch of the first 3-D printed medication (fiercedrugdelivery.com)
3-D printed medicine specialist Aprecia Pharmaceuticals announced that it has completed a $35 million financing round...The move should help...Aprecia commercialize the first FDA-approved 3-D printed drug, Spritam (levetiracetam), a reformulated, easy-to-swallow med for the treatment of epilepsy. The launch is expected to occur in the first half of this year...Aprecia has exclusive rights to utilize Powder-liquid 3DP, a 3-D printing technology developed by MIT in the 1980s. The technique enables the company's ZipDose delivery platform. By printing a tablet consisting of layers of powder, Aprecia drugs can achieve a high degree of dissolvability in liquid. That means dosages as high as 1,000 mg will disintegrate in liquid...The new manufacturing methodology could also facilitate decentralized drug manufacturing and customization of medications to the needs of individual patients.
- Redwood City opens food pharmacy for low-income diabetes patients (ktvu.com)
A very different kind of pharmacy opened in Redwood City on Wednesday. It's called a food pharmacy and is designed to encourage low-income people suffering with diabetes, to eat a healthy diet...It's the first of its kind ever to open in California...With a doctor's prescription, low-income diabetes patients can get food at this special pantry inside the Samaritan House Health Clinic, for free...The food is donated by the Second Harvest Food Bank, which says diabetes and other diseases run rampant among low-income people who often can't afford to eat healthier, or don't know how..."At Second Harvest, our clients have told us that one out of every three adults that we serve are suffering from diabetes. That's more than three times the national average. So it is a big problem among low-income communities," said Kathy Jackson, director of the food bank...The food pharmacy officially opened on Wednesday as a pilot program expecting to provide 100 diabetes patients with a ticket to healthier eating habits...Doctors say the cost of food is a lot less than the cost of treating the effects of a worsening disease.
- Could Preemptive Pharmacogenomic Testing Emerge as an MTM Best Practice? (pharmacytimes.com)
Modern technology is now making genomic testing possible for a fraction of the time and cost..Now pharmacists and physicians can use pharmacogenomic test results to help choose safer and more effective medications for their patients...Pharmacists are undoubtedly the pharmacokinetic experts and the most educated health care providers in regard to the cytochrome P450 system. Preemptive genotyping would make a nice addition to a pharmacy’s list of service offerings and point-of-care testing panel...A clinical consultant pharmacist could use pharmacogenomic testing to guide therapy decisions and decrease drug–drug interactions. This has the potential to save countless health care dollars lost to ineffective medication use, adverse drug events, and hospital readmissions...There are also financial benefits for the testing pharmacy. Looking at pharmacogenomic testing from a medication therapy management perspective, one can imagine the usefulness of integrating genomic testing into a patient’s comprehensive medication review...to make specific evidence-based recommendations to improve patient care.
- Proven cost savings in elderly patients
- Help in predicting and preventing adverse drug reactions
- Decreased hospitalizations due to treatment failure
- Prevention of “trial-and-error” prescribing
Pharmacists are the experts on medication safety and effectiveness, and should be ready to take on the role of personalized medication consultants...Innovation is essential if pharmacy wants to act on new clinical service opportunities and earn a seat at tomorrow’s health care table. We need to be proactive in seeking out new niches...
- McKesson introduces clinical programs platform (chaindrugreview.com)
McKesson Pharmacy Systems & Automation has released the McKesson Clinical Programs Solution, a new platform that enables pharmacists to build customized wellness programs...the Clinical Programs Solution also allows pharmacists to maintain vendor programs for patients with specific medical conditions and saves time and labor costs by automatically synchronizing the data of patients enrolled in a clinical program with McKesson’s EnterpriseRx pharmacy management system...The Clinical Programs Solution offers a wide range of program management capabilities, including a patient-centric view of a patient’s programs and information, real-time notification if a patient is eligible for a clinical program when a prescription is being filled with EnterpriseRx, and a central platform for pharmacies with multiple locations to manage all of their clinical programs.
- Ancient medicinal clay shows promise against today’s worst bacterial infections (worldpharmanews.com)Kisameet Clay Exhibits Potent Antibacterial Activity against the (mbio.asm.org)
Naturally occurring clay from British Columbia, Canada - long used by the region's Heiltsuk First Nation for its healing potential - exhibits potent antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens, according to new research from the University of British Columbia...The researchers recommend the rare mineral clay be studied as a clinical treatment for serious infections caused by ESKAPE strains of bacteria (Enterococcus faecium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species) - cause the majority of U.S. hospital infections and effectively 'escape' the effects of antibacterial drugs...Infections caused by ESKAPE bacteria are essentially untreatable and contribute to increasing mortality in hospitals...After 50 years of over-using and misusing antibiotics, ancient medicinals and other natural mineral-based agents may provide new weapons in the battle against multidrug-resistant pathogens..