- The Quest for a Vaccine Against a Killer Bug (bloomberg.com)A New York Giants player is in danger of having his foot amputated (news.yahoo.com)
Pfizer is targeting a deadly bacterium that thrives in hospitals…Staphylococcus aureus can strike healthy, young people with no known risk factors, survive a barrage of antibiotics, and sometimes be fatal…One antibiotic-resistant strain frequently found in hospitals (MRSA) is responsible for about 75,000 serious infections and 10,000 deaths…a year…The pharmaceutical giant has spent more than 15 years working on a vaccine…and is in the midst of testing it on patients…Staph is a very difficult organism to make a vaccine against...Pfizer’s researchers are trying a multipronged approach. Two of the vaccine’s components go after a capsule that cloaks the bacterium and prevents the immune system from recognizing it. Another deprives the organism of manganese…A fourth targets the mechanism staph uses to lodge itself in the body…
- ICD-10 Could Challenge Emergency Rooms (pharmacytimes.com)
…changeover to ICD-10 medical diagnosis codes could complicate tasks in emergency departments…researchers...looked at more than 24,000 clinical encounters in the emergency room, they found that nearly a quarter could be assigned incorrect ICD-10 codes…also…27% of 1830 ICD-9 indicator codes commonly used by emergency physicians had convoluted mappings to ICD-10 codes that could pose problems for clinical documentation, reimbursement, disease reporting, and justifying hospital admissions…Depending on the analytic programs that the pharmacies use to predict how much medications to store and how complex the transition to ICD-10 is, pharmacies might have shortages of medications due to inaccurate reports and algorithms..
- Drug tested in Vegas shows promise in relieving agitation in Alzheimer’s patients (reviewjournal.com)Effect of Dextromethorphan-Quinidine on Agitation in Patients With Alzheimer Disease DementiaA Randomized Clinical Trial (jama.jamanetwork.com)
Encouraging results from a drug trial to reduce agitation often felt by Alzheimer's patients and led by the director (Dr. Jeffrey Cummings) of the Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health in Las Vegas were published…Journal of the American Medical Association…study tested the drug AVP-923 in participants with Alzheimer's disease and moderate-to-severe agitation…drug's success so far in the DM/Q trial will prompt a clinical phase…"The effects from the DM/Q trial were remarkable and one of the strongest we've ever seen," said… director of the Ruvo center, who led the study. "Usually it takes at least three weeks to see a change, but in this case, our participants started experiencing benefits within one week."
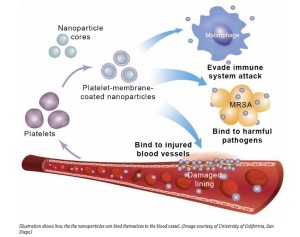
- Cloaked Nanoparticles Pave Way For Targeted Drug Delivery (forbes.com)Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking (req sub) (nature.com)Nanotechnology: Platelet mimicry (req sub) (nature.com)
A study from the University of California,…Jacobs School of Engineering shows how nanoparticles can be an effective delivery system for drugs in the treatment of cardiovascular disease and systemic bacterial infections…engineers disguised nanoparticles as human platelets to see if they could increase the healing power of drug treatments by delivering those drugs to targeted areas in the body or organs…By using the natural biology of our bodies with the nanoparticle technology, the researchers have taken advantage of the unique natural properties of human platelet membranes for a new form of drug delivery.
- Reducing LDL with PCSK9 Inhibitors — The Clinical Benefit of Lipid Drugs (nejm.org)
…Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration…met to consider marketing applications for the new molecular entities alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha)on the basis of their ability to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels…These first-in-class medications are fully humanized monoclonal antibodies that inactivate proprotein convertase subtilisin–kexin type 9…consequent lowering of LDL cholesterol levels…has led to optimism regarding the potential — but as yet unproven — cardiovascular benefits…LDL cholesterol reduction as the surrogate measure of clinical benefit. No efficacy data on cardiovascular outcomes were provided…Establishing evidence of improved cardiovascular outcomes is key to evaluating medications from any new drug class intended to reduce such risk….definitive evidence of reduced cardiovascular event rates is essential…to provide such evidence should elucidate the medications' true clinical benefits and possible risks.
- 7,000 scientists. 100 years. One lifesaving treatment. (washingtonpost.com)100 Years to Find a Cure: Can the Process be Accelerated? (gladstone.org)
Here's the CliffsNotes version of how most drugs go from idea to reality: Basic academic research provides the foundation for a series of clinical trials, first in animals and then in humans, which eventually tell us whether a new treatment is safe and effective…the reality of drug development is rarely that linear or precise…the path to creating a life-saving treatment can be an extremely long, labor-intensive effort that involves thousands of scientists over many decades...
- Stanford team re-engineers virus to deliver therapies to cells (news.stanford.edu)
Researchers stripped a virus of its infectious machinery and turned its benign core into a delivery vehicle that can target sick cells while leaving healthy tissue alone….totally redesigned its core to repurpose its infectious capabilities into a safe vehicle for delivering vaccines and therapies directly where they are needed…"We call this a smart particle,"…. "We make it smart by adding molecular tags that act like addresses to send the therapeutic payload where we want it to go." Stanford has patented the technology and different aspects are licensed to a biotechnology company… no timetable for commercial development.
- Beating parasites wins three scientists Nobel prize for medicine (reuters.com)
Three scientists…whose discoveries led to the development of potent new drugs against parasitic diseases…won the Nobel Prize for Medicine…Irish-born William Campbell and Japan's Satoshi Omura won half of the prize for discovering avermectin,…used to treat..river blindness and lymphatic filariasis...China's Tu Youyou was awarded the other half of the prize for discovering artemisinin, a drug that has slashed malaria deaths…She is China's first Nobel laureate in medicine.
- Analysis shows pharma is getting better at R&D (mmm-online.com)
A new analysis of pharma research and development data shows that drugmakers have become increasingly successful in identifying the right candidates for drug development and getting them to market in recent years…From 2010 to 2014, one out of every 13 drugs in phase-I development came to market—compared to one of 19 phase-I drug candidates making it from 2007 to 2011,…Developing a drug takes 10 years on average currently, which is 40% longer than it took 15 years ago…Drug discovery—defined as all the work leading up to human clinical trials—has remained steady, taking four years on average.
- Pharmacists Reduce HIV Drug Interactions (pharmacytimes.com)
Thanks to the introduction of antiretroviral therapy, HIV-infected individuals are living longer than ever before,…this advancement means those with HIV are living long enough to experience aging’s comorbidities. They are also at higher risk for medication errors…as ART is associated with greater polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions…medication errors can increase viral resistance by decreasing ART levels, or increase risk of toxicity by elevating concentrations. Because of this, pharmacists are critical for preventing drug-drug interactions and other medical errors in HIV-infected hospital patients..