- Nearly 800 Dietary Supplements Tainted With Unapproved Ingredients Such As Viagra And Steroids (techtimes.com)
...researchers of a new study published in JAMA Network Open found that nearly 800 dietary supplements were found to be adulterated with unapproved drugs. Specifically, from 2007 to 2016, there were 776 dietary supplements identified to contain one or more hidden drug ingredients, implicating 146 dietary supplement companies...Most of the adulterated dietary supplements were marketed for sexual enhancement, weight loss, and muscle building. The most common hidden drug ingredient in sexual enhancement supplements is sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, while the most common additive in weight loss supplements is banned weight-loss drug sibutramine, and synthetic steroid drugs for the muscle building supplements...experts are now urging the FDA to take urgent action to have these products removed from the market. Such products pose serious health risks, especially to users who are unaware that the supplements they are taking are actually adulterated with drugs...
- About 1 in 5 hospitals mark up drug prices at least 700 percent, study finds (healthcarefinancenews.com)
Nearly one in five hospitals mark up medicine prices 700 percent or more, according to a new analysis from The Moran Company, prepared for The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America...This means that if a hospital purchased a medicine for $150, a 700 percent markup could result in patients being billed $1,050, according to the study. And the analysis also found that 320 hospitals – eight percent of those included in the study – marked up some medicine prices more than 1,000 percent...The analysis used Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services data that included total costs and charges for all medicines from 3,792 hospitals. On average, those hospitals marked up the price of medicines nearly 500 percent, consistent with an analysis of 20 medicines previously conducted by Moran...Markups on medicine prices often lead to higher reimbursement by health plans. More than half of commercial payers reimburse hospital outpatient departments as a percent of billed charges. Hospitals have incentives to increase markups as higher charges are associated with greater profitability...
- Mount Sinai’s medical school opens blockchain research center (medcitynews.com)
...blockchain technology has moved from cryptocurrency to other fields…The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Institute for Next Generation Healthcare opened the Center for Biomedical Blockchain Research...with the aim of developing partnerships with companies looking to apply the technology to clinical medicine and biomedical research…Researchers have also been seeking to apply the technology to clinical trials...the British Medical Journal concluded that blockchain provides a significant opportunity for clinical research because it can help structure more transparent, checkable methodology and, under certain conditions, check clinical trial integrity...Imperial College London played host to a hackathon specifically to explore the use of blockchain in clinical trials...to replace the operations of contract research organizations...The two finalists proposed using distributed ledger technologies to operate all the necessary transactions between drug companies running trials and the clinical trial sites where they take place...
- A serious new hurdle for CRISPR: Edited cells might cause cancer, two studies find (statnews.com)CRISPR stocks tank after research shows edited cells might cause cancer (cnbc.com)
Editing cells’ genomes with CRISPR-Cas9 might increase the risk that the altered cells, intended to treat disease, will trigger cancer, two studies published on Monday warn — a potential game-changer for the companies developing CRISPR-based therapies...scientists found that cells whose genomes are successfully edited by CRISPR-Cas9 have the potential to seed tumors inside a patient. That could make some CRISPR’d cells ticking time bombs...The CEO of CRISPR Therapeutics, Sam Kulkarni, told STAT the results are “plausible.” Although they likely apply to only one of the ways that CRISPR edits genomes (replacing disease-causing DNA with healthy versions) and not the other (just excising DNA), he said, “it’s something we need to pay attention to...We need to do the work and make sure edited cells returned to patients don’t become cancerous.”...Standard CRISPR-Cas9 works by cutting both strands of the DNA double helix. That injury causes a cell to activate a biochemical first-aid kit orchestrated by a gene called p53, which either mends the DNA break or makes the cell self-destruct...The flip side of p53 repairing CRISPR edits, or killing cells that accept the edits, is that cells that survive with the edits do so precisely because they have a dysfunctional p53 and therefore lack this fix-it-or-kill-it mechanism...The reason why that could be a problem is that p53 dysfunction can cause cancer...P53 mutations are responsible for nearly half of ovarian cancers; 43 percent of colorectal cancers; 38 percent of lung cancers; nearly one-third of pancreatic, stomach, and liver cancers; and one-quarter of breast cancers...
- Hey, pharma: Data’s more than a ‘defense mechanism,’ ad executive says (fiercepharma.com)
...most pharma companies have begun to use data to make marketing decisions, one healthcare agency data veteran sees a recurring problem in the way that data is typically utilized...Pharma marketers too often only use data after the fact, said Kevin Troyanos...Saatchi & Saatchi Wellness. While post-campaign ROI analysis is important to find out what worked and what didn’t for the next effort, it can also lead to confirmation bias...That’s when data is used to validate the HiPPO—Highest Paid Person’s Opinion..True data-driven companies use information dynamically to inform decisions, identify what works and what doesn’t work and to make changes on the fly...Pharma typically puts a lot of research into one tactic, one channel or one creative and are almost locked in to it. What happens then is that teams are leveraging data in a defensive way, essentially using it to say that the decision they made was the right one and this is why,” he said. “Pharma needs to begin to use data as a driver, not as a defense mechanism.”...
- Financial disclosure lacking in publication of clinical trials, new research shows (healthcarefinancenews.com)
It's the first study to examine financial conflict of interest in publication of clinical trials that underpin FDA approval of new oncology drugs...A substantial proportion of pharmaceutical industry payments to authors of oncology clinical trials published in major scientific journals are not disclosed, new research shows. The publications focused on clinical trials that tested new cancer drugs...Authors of the research letter examined the federal Open Payments Database to determine payments to oncologists who authored studies in high-impact journals...They then cross-checked the information to determine whether the authors properly disclosed the funding when the results of their clinical trials were published in scientific journals. Depending on the journal, almost half of total funding was not disclosed...
- EMA Report: Clinical Data Published on 50 Medicines in One Year (raps.org)European Medicines Agency Clinical Data: Online Access to Clinical Data for Medicinal Products for Human Use (clinicaldata.ema.europa.eu)Clinical data publication ( Policy 0070) report Oct 2016 - Oct 2017 (ema.europa.eu)
The European Medicines Agency...published its first report on implementing its policy on the publication of clinical data whereby researchers, academics and others can access data from clinical reports submitted by pharmaceutical companies to EMA for new medicines as of 1 January 2015...The 27-page report covers one year from the launch of EMA’s clinical data website on 20 October 2016, and lists the 50 medicines for which clinical data were published...EMA is the only regulatory authority to provide open access to clinical data submitted by companies in support of their marketing authorisation applications...The report unveils the documents published, the amount of commercially confidential information redacted and the anonymization techniques used...EMA accepted about one third of CCI redactions proposed by pharmaceutical companies, though only 0.01% of 1.3 million pages published contained CCI redactions...anonymization techniques to protect personal data, the report suggests conducting a “proper assessment” of the impact of the anonymization technique on data utility and improving the quality of the anonymization reports...
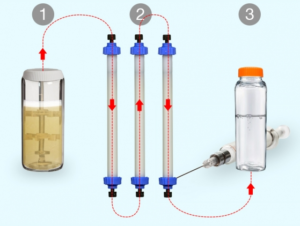
- A new way to manufacture small batches of biopharmaceuticals on demand (news.mit.edu)
Biopharmaceuticals, a class of drugs comprising proteins such as antibodies and hormones, represent a fast-growing sector of the pharmaceutical industry. They’re increasingly important for “precision medicine” — drugs tailored toward the genetic or molecular profiles of particular groups of patients...Such drugs are normally manufactured at large facilities dedicated to a single product, using processes that are difficult to reconfigure. This rigidity means that manufacturers tend to focus on drugs needed by many patients, while drugs that could help smaller populations of patients may not be made...To help make more of these drugs available, MIT researchers have developed a new way to rapidly manufacture biopharmaceuticals on demand. Their system can be easily reconfigured to produce different drugs, enabling flexible switching between products as they are needed...Traditional biomanufacturing relies on unique processes for each new molecule that is produced...We’ve demonstrated a single hardware configuration that can produce different recombinant proteins in a fully automated, hands-free manner...
- How IBM and the CDC are testing blockchain to track health issues like the opioid crisis (fastcompany.com)HIT Think How blockchain could solve 4 major problems in healthcare (healthdatamanagement.com)
IBM and CDC experts are hopeful that using a blockchain could help streamline long-running surveys that track patient symptoms and treatments...The Centers for Disease Control and IBM are collaborating on a blockchain-based system that could track public health issues like the ongoing opioid crisis...The new system, which IBM and the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics have tested using simulated data, could make it easier for the CDC to survey medical providers about data like the reasons patients visit and the symptoms they display...Using the blockchain approach could make it easier to automatically collect the data, keep it secure, and log who’s accessed which parts of it...“There’s a lot of transparency that blockchain seems to offer to us,”...Blockchains are perhaps still most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies, where the secure digital ledgers are used to track who owns each unit of currency, with copies of the ever-growing chain of records automatically duplicated to anyone who wants them. But companies like IBM and Microsoft are exploring how the technology can be used in more traditional industries to sync up data like logs and transaction records between business associates, like health providers and the CDC. The automatic data replication can help maintain a reliable audit trail for more than just digital currency, they say...
- Clinical technology is broken, so what is being done to fix it? (outsourcing-pharma.com)
The need to improve visibility, enable faster study execution, and improve study quality, is driving the industry to unify its "broken" clinical trial operating environments, according to a report...nearly all respondents reported a need to unify clinical trial operating environments, and 87% said they have or plan to have, an initiative in motion to fulfill this need and improve trial performance...The main challenge of siloed applications and processes is integrating multiple applications...The top drivers for unification are to improve visibility (75%), enable faster study execution (61%), and improve study quality (60%)...The majority of respondents (84%) reported “significant deficiencies” with their current clinical trial management system (CTMS) applications, with more than 85% citing the inability to fully support functions such as governance and oversight, resource management, as well as issue and task management...industry is recognizing the need for key performance metrics (KPIs) and reporting capabilities “to learn about how they operate so that they can improve...recognizing they need a unified technology...